understanding relay electrical diagrams: a comprehensive overview
Release time:2026-01-18 07:46:38
Relays have become an integral component in electrical and electronic circuits, acting as automated switches that enable the control of a larger power supply or device with a lower power signal. To make the effective use of relays in various applications, understanding the relay electrical diagram is essential. A relay electrical diagram provides a visual representation of how a relay operates within a circuit, highlighting the components involved and their interconnections. This article will discuss the basic elements of relay electrical diagrams, their significance, and how they function in real-world applications.
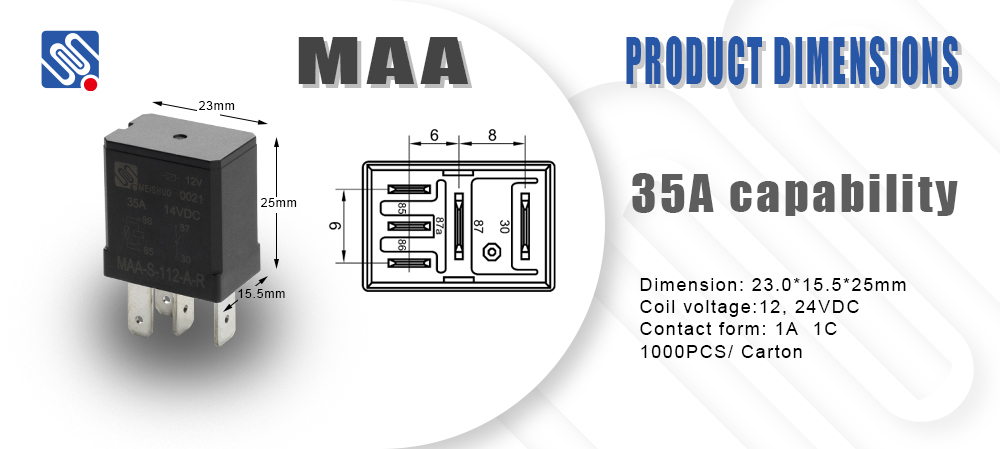
What is a Relay?
A relay is an electromechanical switch that allows one circuit to control another. It typically consists of an electromagnetic coil, an armature, a spring, and a set of contacts. When electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that pulls the armature, thereby opening or closing the contacts. Relays can be found in various types and configurations, including electromechanical relays, solid-state relays, and time-delay relays, each serving distinct purposes in electrical systems.
Key Components of Relay Electrical Diagrams
Relay Symbol: In the electrical diagram, relays are often represented by a standardized symbol that consists of a rectangular box with lines indicating the terminals. Understanding this symbol is crucial, as it allows one to identify the relay component within the circuit.

